Autonomy is important. We all want the ability to choose how and where we will spend the later years of our lives. Many Americans are now choosing to remain at home, or “Age in Place”.
It’s an increasingly popular lifestyle choice. According to AARP, 87 percent of adults over the age of 65 want to stay in their current home and community as they age. Over 70 percent of adults between 50 and 64 years old want to age in place.
It makes sense. Homes are full of memories, and they come to embody the character of their owners. Plus, staying at home preserves connections to family, friends, and the local community.
One of the greatest health challenges of aging in place is fall prevention. For those older adults who want to remain at home, assess your current and future needs. Is your home safe? Does it need remodeling?
An Occupational Therapist is a professional who can assess home safety and recommend designs and/or devices to prevent injury and disability. The goal is to promote the resident’s health and help the person develop, retain, or improve their level of independence.
The Risks of Falls
IN THIS ARTICLE
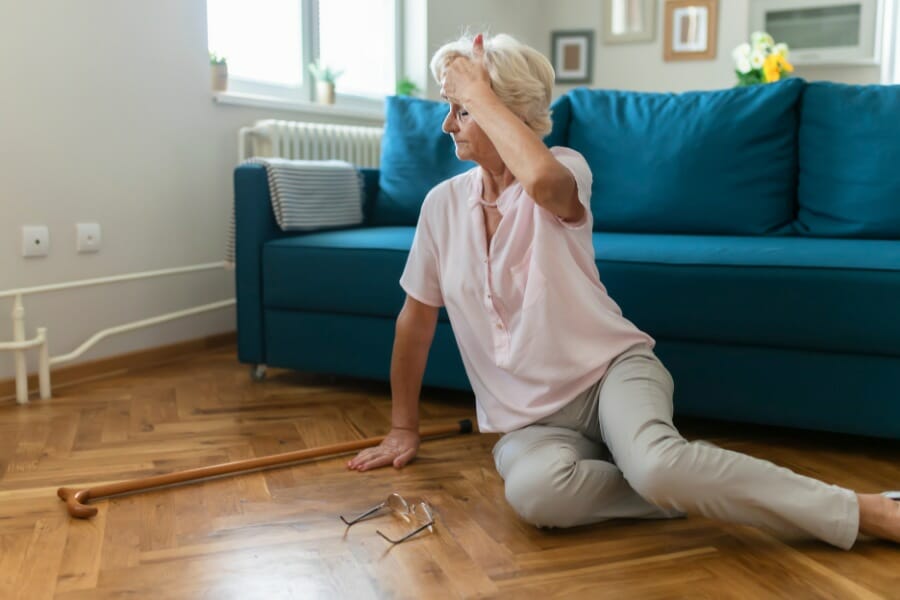

Falls are a serious concern for older adults, as they can result in injuries such as hip fractures, broken bones, and head trauma. In fact, falls are the leading cause of injury-related hospitalization among seniors. Falls can also lead to long-term disability, chronic pain, and decreased quality of life.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of falling among seniors. These include:
- Medications: Certain medications can cause dizziness, drowsiness, or other side effects that increase the risk of falling.
- Vision problems: Poor vision can make it difficult to navigate one’s surroundings and avoid obstacles.
- Home hazards: Cluttered or poorly lit environments can increase the risk of tripping and falling.
- Chronic health conditions: Conditions such as arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke can affect balance and coordination.
- Muscle weakness: Loss of muscle mass and strength can make it more difficult to maintain balance and prevent falls.
It is important for older adults and their caregivers to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to mitigate them. This may include modifying the home environment, addressing vision or health issues, and reviewing medications with a healthcare provider. By taking proactive steps to prevent falls, seniors can reduce their risk of injury and maintain their independence.
Here are some of the most important factors in preventing falls.
1. Check medication side effects and interactions.
Some medicines may cause dizziness or balance issues—like blood pressure pills and diuretics—which increases a person’s likelihood of falling.
2. Attend regular check-ups.
Balance and vision problems contribute to a majority of falls. Keep up-to-date on medications and prescriptions for eye health. A private duty nurse or home health nurse can reconcile medications and check for interactions if needed.
Seniors should have their vision checked regularly to ensure that they can see clearly and have no vision problems that could increase their risk of falling. Seniors who wear glasses should make sure their prescription is up to date.
3. Get stable flooring and shoes.
Plastic runners are often better than carpets. If you do have rugs or carpets, make sure they are tacked down and won’t slip around. Try wearing low-heeled shoes or use a rubber-tipped cane. Avoid socks, slippers, or anything that could lead to slipping and falling.
4. Install hardware.
Seniors should take steps to make their homes safer to reduce their risk of falling. Some tips for home safety include:
- Removing clutter and tripping hazards from walkways
- Installing handrails on stairs and in bathrooms
- Using non-slip mats in the shower or bathtub
- Ensuring that rooms are well-lit
The bathroom can be one of the most dangerous places because it is one of the most slippery. Put down a non-slip mat in the shower. You may also want to consider adding grab bars in the shower and in other areas of the house. (An Occupational Therapist can be very helpful in determining the most effective areas to put up support bars, and other modifications.)
5. Add adequate lighting.
If you do have vision problems, it is incredibly important to make sure the house is well-lit—especially around the stairs.
Another way to combat stairs or other changes in depth is to create contrast with different colors.
6. Footwear
Seniors should wear footwear that is comfortable, supportive, and non-slip. Shoes with a low heel and a non-slip sole are a good choice.
7. Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help seniors improve their balance, strength, and flexibility, which can reduce their risk of falling. Seniors should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week. Some good options for seniors include:
- Walking
- Tai chi
- Yoga
- Strength training
- Balance exercises
Seniors should talk to their doctor before starting a new exercise program.
8. Medications
Seniors should talk to their doctor or pharmacist about any medications they are taking that could increase their risk of falling. Some medications can cause dizziness or drowsiness, which can increase the risk of falling.
Identifying Fall Hazards
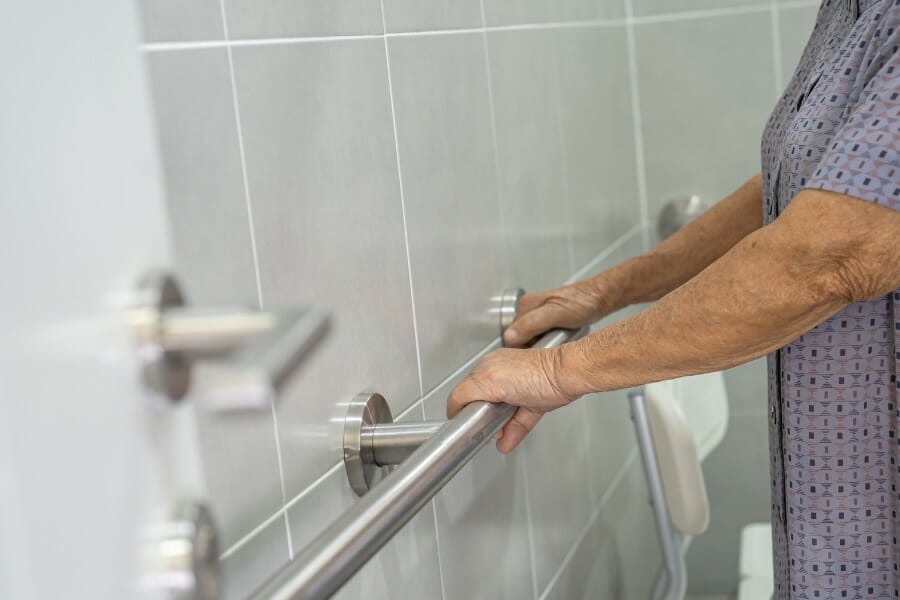

Preventing falls among seniors starts with identifying fall hazards in their environment. Seniors and their caregivers should conduct a thorough assessment of their living space to identify potential hazards. Here are some common fall hazards and how to address them:
Tripping Hazards
Tripping hazards are one of the most common causes of falls among seniors. Seniors should remove any objects that are blocking their path, such as cords, rugs, and clutter. Rugs should be secured with double-sided tape or slip-resistant backing to prevent them from slipping.
Home Hazards
Seniors should also be aware of potential hazards in their home, such as loose floorboards, uneven surfaces, and stairs without handrails. These hazards should be addressed as soon as possible to prevent falls.
Handrails and Grab Bars
Handrails and grab bars can be installed in areas where seniors are most likely to fall, such as bathrooms and stairways. These safety features can provide seniors with the support they need to maintain their balance and prevent falls.
Light Switches
Seniors should be able to easily access light switches in their home. They should also ensure that there is adequate lighting in all areas of their home, especially in stairways and hallways.
Foot Problems and Disorders
Seniors with foot problems or disorders, such as arthritis or neuropathy, should wear properly fitting shoes with non-slip soles. They should also consider using assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, to help them maintain their balance.
By identifying fall hazards and taking steps to address them, seniors can reduce their risk of falling and maintain their independence.
Role of Assistive Devices
Assistive devices can play a crucial role in preventing falls among seniors. These devices are designed to improve balance, reduce pain, increase mobility and confidence, and decrease the risk of falls.
One of the most common types of assistive devices used by seniors are mobility aids such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs. These devices can help seniors maintain their balance and stability while walking, and reduce the risk of falls. When selecting a mobility aid, it is important to choose the correct device that fits the individual’s needs and physical abilities.
In addition to mobility aids, hearing aids can also play a role in preventing falls among seniors. Studies have shown that hearing loss can increase the risk of falls by impairing a person’s ability to detect sounds and maintain balance. By using a hearing aid, seniors can improve their ability to hear and maintain their balance, reducing the risk of falls.
It is important to note that while assistive devices can be helpful in preventing falls, they should not be relied upon as the sole solution. Seniors should also take other preventative measures such as exercising regularly, having regular vision and hearing check-ups, and making their home environment safer by removing tripping hazards and installing grab bars and handrails.
Preventing Falls in the Elderly
The above tips will help you fall-proof your home.
Aging in place can be successful if you are prepared. Take control of your independence and quality of life with a long-term care plan and the support of local aging professionals.
A health care provider or private duty nurse can assist seniors who want to age in place at their residence and continue living their daily lives safely. Elderly individuals do not have to risk hip fractures and head injuries or give out their love of hobbies and outdoor activities.
Care for falls is available, but it is much better to simply prevent the risk of falls.
Click below to discover how an in-home private nurse from NurseRegistry could benefit the life of your elderly loved one today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some effective fall prevention strategies for seniors?
There are several effective fall prevention strategies that seniors can adopt to reduce their risk of falls. These include:
- Regular exercise to improve strength, balance, and flexibility.
- Making modifications to the home environment, such as removing tripping hazards and installing grab bars in the bathroom.
- Reviewing medications with a healthcare provider to identify any that may increase fall risk.
- Getting regular vision and hearing check-ups.
- Wearing appropriate footwear with non-slip soles.
What devices can be used to prevent falls among the elderly?
There are several devices that can be used to prevent falls among the elderly, including:
- Walkers or canes to assist with balance and mobility.
- Hip protectors to reduce the risk of hip fractures in the event of a fall.
- Bed rails and bed assist handles to help seniors get in and out of bed safely.
- Alert systems that can be worn as a pendant or bracelet and used to call for help in the event of a fall.
What are the risk factors for falls in seniors?
There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of falls among seniors, including:
- Muscle weakness and balance problems.
- Chronic health conditions such as arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, and dementia.
- Medications that can cause dizziness or drowsiness.
- Environmental factors such as poor lighting, cluttered walkways, and slippery floors.
- Poor vision or hearing.
What are some exercises seniors can do to prevent falls?
Seniors can do several exercises to improve their balance, strength, and flexibility, including:
- Tai Chi, which has been shown to improve balance and reduce fall risk.
- Yoga, which can improve strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Resistance training using weights or resistance bands to improve muscle strength.
- Walking, which can improve overall fitness and reduce fall risk.
What are some interventions that can be implemented to prevent falls among seniors?
In addition to the strategies and devices listed above, there are several other interventions that can be implemented to prevent falls among seniors, including:
- Home safety assessments to identify and address potential fall hazards.
- Referral to physical therapy or occupational therapy for fall prevention interventions.
- Medication review and management to reduce fall risk.
- Education and training for seniors and their caregivers on fall prevention strategies and risk factors.
What are the consequences of falls in the elderly?
Falls in the elderly can have serious consequences, including:
- Fractures, particularly of the hip, which can lead to loss of independence and reduced quality of life.
- Traumatic brain injuries, which can cause long-term cognitive impairment.
- Fear of falling, which can lead to social isolation and decreased physical activity.
- Increased healthcare costs and hospitalizations.