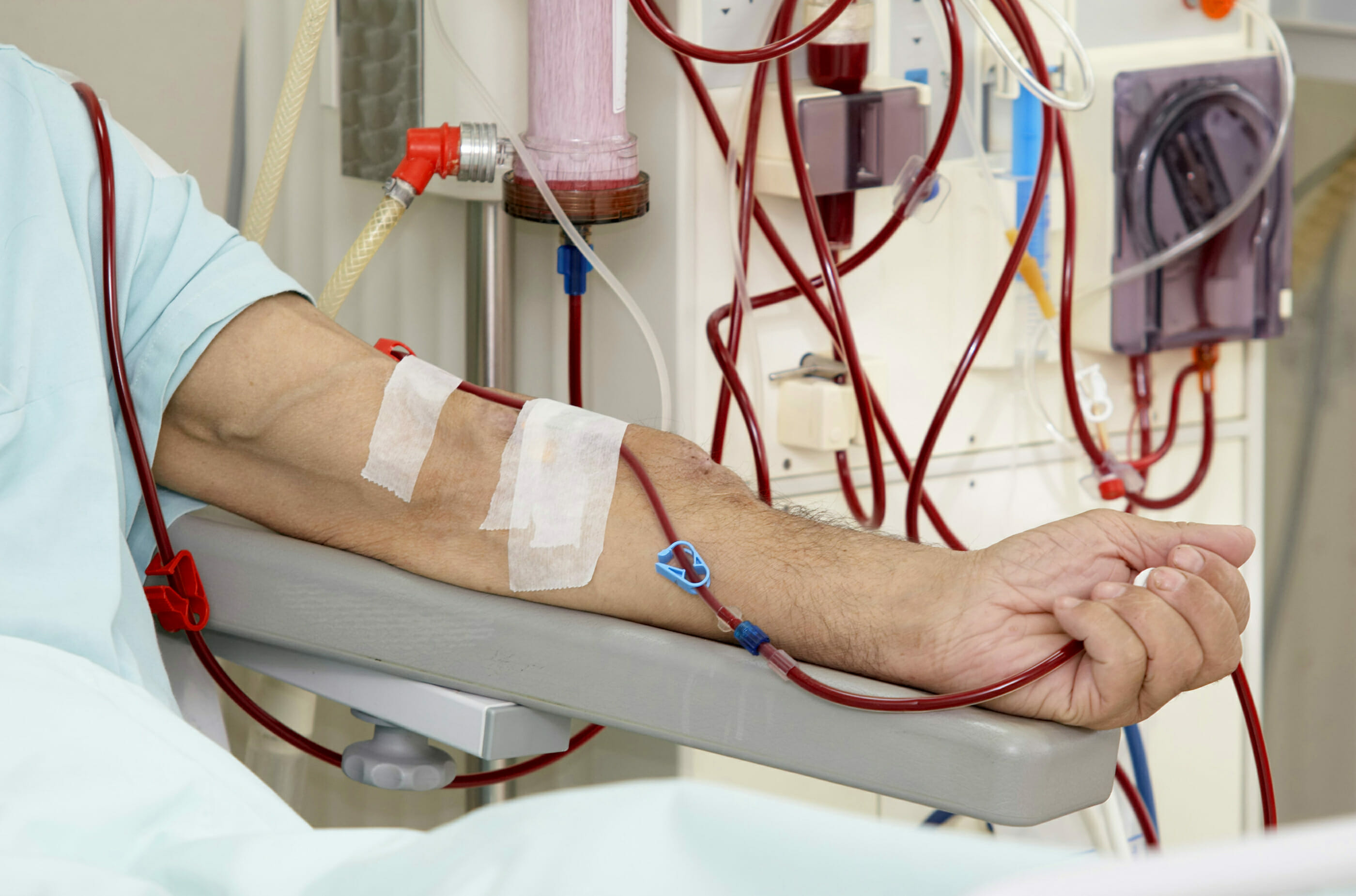
What is Kidney Disease: CKD Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Kidney disease is a condition that affects the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine.
When the kidneys are damaged, they may not work properly, leading to a buildup of waste products in the blood and other complications. There are different types of kidney disease, but the most common one is chronic kidney disease (CKD).
CKD is a long-term condition that can progress over time, sometimes leading to kidney failure. It can be caused by various factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and other underlying health conditions.
Symptoms of chronic kidney disease may include fatigue, swelling in the legs, high blood pressure, and changes in urination patterns. Early detection and treatment of CKD are important to slow down the progression of the disease and prevent complications.
Understanding kidney disease and its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can help individuals and their loved ones manage the condition and improve their quality of life.
It is also important to know how to prevent kidney disease and manage risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
Key Takeaways
- Kidney disease affects the kidneys’ ability to filter waste products from the blood and produce urine.
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most common type of kidney disease and can progress over time, leading to kidney failure.
- Early detection and treatment of CKD are important to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
What is Kidney Disease?
IN THIS ARTICLE
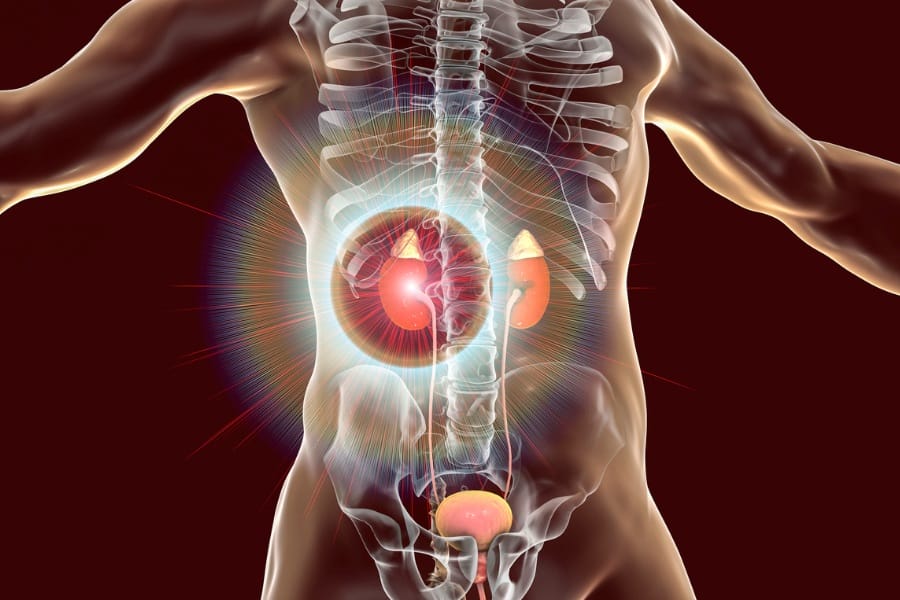
Kidney disease is a condition that affects the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and removing them from the body through urine.
When the kidneys are damaged, they cannot filter blood properly, which can lead to a buildup of waste products and fluids in the body.
Causes of Kidney Disease
There are several causes of kidney disease, including chronic conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Other conditions that can cause kidney disease include polycystic kidney disease, lupus, glomerulonephritis, and IgA nephropathy. Additionally, acute kidney injury can also lead to kidney disease.
Types of Kidney Disease
There are several types of kidney disease, including chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is a progressive condition that can lead to kidney failure.
Other types of kidney disease include acute kidney injury, which is a sudden and often reversible condition, and kidney stones, which are hard deposits that form in the kidneys.
Stages of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease is typically classified into five stages, with stage one being the mildest and stage five being the most severe, including loss of kidney function.
In the early stages of kidney disease, there may be no noticeable symptoms, but as the condition progresses, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, and swelling may occur. In the later stages of kidney disease, patients may require dialysis or a kidney transplant to manage the condition.
Let’s look at symptoms a little more indpeth.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the Symptoms
Kidney disease often goes unnoticed until it has progressed to a more advanced stage. However, there are some symptoms that may indicate the presence of kidney disease. These include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Changes in urination, such as frequency, color, or amount
- Itchy skin
- Trouble sleeping
- Muscle cramps or twitches
If any of these symptoms are present, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Diagnostic Tests
There are several tests that can be used to diagnose kidney disease. These include:
- Blood tests: A blood test can measure the levels of creatinine and other waste products in the blood cells. High levels of these substances can indicate poor kidney function.
- Urine tests: A urine test can detect the presence of protein and other substances that should not be present in urine. This can indicate kidney damage.
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR): This test measures how well the kidneys are filtering waste from the blood. A low GFR can indicate kidney damage.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scan, can provide a picture of the kidneys and help detect any abnormalities.
- Kidney biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of kidney tissue may be removed for examination under a microscope. This can help diagnose certain types of kidney disease.
It is important to note that not all tests may be necessary for every individual. The healthcare provider will determine which tests are appropriate based on the individual’s symptoms and medical history.
Kidney Disease Treatment Options
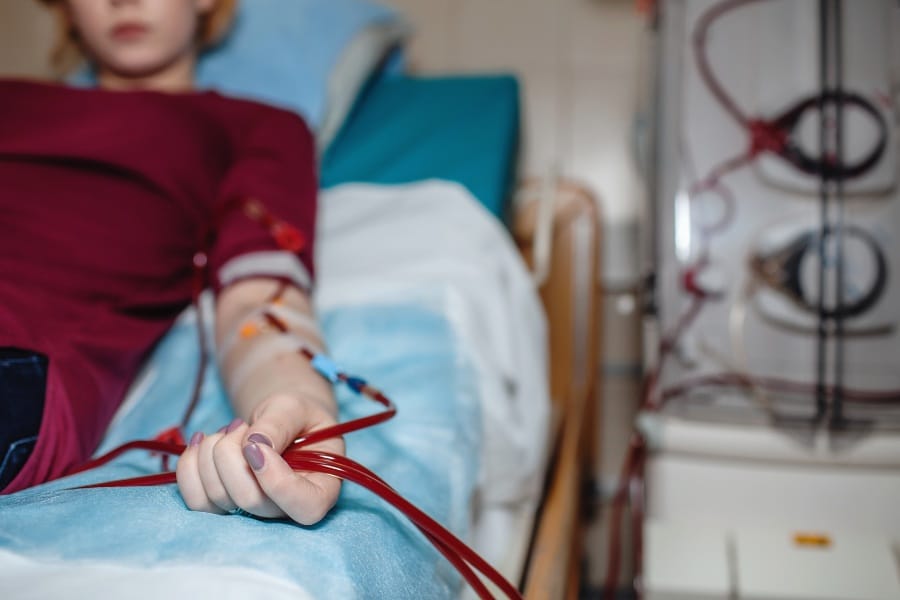
Kidney disease is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent complications and maintain overall health.
There are several treatment options available for kidney disease, including medical treatments, lifestyle and home remedies, and kidney transplants.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments for kidney disease include medications to control blood pressure, reduce proteinuria, and manage other symptoms.
Blood pressure control is particularly important, as high blood pressure can damage the kidneys further. Medications such as ACE inhibitors and ARBs can help control blood pressure and reduce proteinuria.
Steroids may also be used to treat kidney disease, particularly in cases where inflammation is present. However, these medications can have side effects and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle and home remedies can also help manage kidney disease.
Maintaining a healthy diet and staying active can help control blood pressure and manage other symptoms. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can also help reduce the risk of complications.
Managing other health conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, is also important for overall kidney health. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can also help prevent further damage to the kidneys.
Kidney Transplant
In cases where kidney function is severely impaired, a kidney transplant may be necessary. Kidney transplantation is a complex procedure that involves replacing a diseased kidney with a healthy one from a donor.
Transplantation can provide a more permanent solution to kidney disease, but it also requires ongoing management to prevent rejection and other complications.
Patients who undergo kidney transplantation must take immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection, and they must be monitored closely by a healthcare professional.
Living with Kidney Disease
Diet and Nutrition
When living with kidney disease, it is important to follow a healthy and balanced diet.
This means limiting foods that are high in sodium, potassium, and phosphorus. Patients should also avoid consuming too much extra water or fluid, as this can put extra stress on the kidneys.
It is recommended that patients work with a dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that meets their specific needs.
Daily Life and Management
Living with kidney disease can be challenging, but there are steps patients can take to manage their condition.
It is important to monitor blood pressure regularly and take any prescribed medications as directed.
Patients should also try to maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly. It is important to avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake, as both can have negative effects on kidney function.
Kidney Friendly Tips
Here are some tips for living with kidney disease:
- Choose lower sodium options when shopping for groceries
- Limit intake of high-potassium foods such as bananas and potatoes
- Avoid high-phosphorus foods such as cheese and processed meats
- Drink water in moderation and avoid sugary drinks
- Take prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider
- Monitor blood pressure regularly and report any changes to a healthcare provider
- Get regular exercise and maintain a healthy weight
It is important for patients with kidney disease to work closely with their healthcare team to manage their condition and prevent complications.
By following a healthy lifestyle and taking prescribed medications as directed, patients can improve their quality of life and reduce their risk of complications such as heart disease and anemia.
Prevention and Risk Factors
Preventing kidney disease is essential for maintaining healthy kidneys. There are several ways to reduce the risk of developing kidney disease, and it is important to take action as early as possible.
Risk Factors
Some of the risk factors for kidney disease include high blood pressure, diabetes, family history of kidney disease, obesity, smoking, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that an individual will develop kidney disease. However, it does increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
Prevention
There are several steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing kidney disease. These include:
- Managing blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney disease. It is essential to monitor blood pressure regularly and take steps to keep it under control.
- Managing diabetes: Diabetes is another leading cause of kidney disease. It is important to manage blood sugar levels and follow a healthy diet and exercise routine.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for kidney disease, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of kidney disease.
- Avoiding certain medications: Some medications can damage the kidneys, and it is important to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
- Getting regular check-ups: Regular check-ups can help detect kidney disease early and prevent further damage.
By managing risk factors and following a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of developing kidney disease and maintain good kidney health.
Get Professional Kidney Disease Care
Individuals suffering from kidney disease are commonly used to medical care and procedures. Why not opt for a private in-home nurse?
NurseRegistry is a trusted nurse staffing agency that perfectly matches you with a compatible nurse who is professional, kind, and skilled.
Plus, your loved one will receive all the care they’d receive at a medical facility or long-term care facility in the comfort of their home, which is a major impact when it comes to quality of life.
Click below to learn more about NurseRegistry.
Frequently Asked Questions about Kidney Disease
What are the common symptoms indicating kidney disease?
Kidney disease often progresses silently, with few or no noticeable symptoms until the later stages. However, some common symptoms of kidney disease include fatigue, weakness, difficulty concentrating, decreased appetite, muscle cramps, and swelling in the feet and ankles. Additionally, changes in urination patterns, such as increased urination at night or foamy urine, may also be signs of kidney disease.
How can one prevent the progression to kidney failure?
Preventing the progression of kidney disease to kidney failure is possible by managing underlying conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can also help prevent kidney disease from progressing.
What are the latest advancements in treating chronic kidney disease?
Recent advancements in treating chronic kidney disease include the use of medications that can slow the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of complications. Additionally, new technologies such as kidney transplant and dialysis have also improved the treatment options available for patients with chronic kidney disease.
What are the stages of chronic kidney disease and their significance?
Chronic kidney disease is divided into five stages based on the level of kidney function. The stages range from mild damage, with normal kidney function, to complete kidney failure. The significance of each stage depends on the individual and their overall health. However, early detection and treatment of kidney disease can slow or prevent the progression of the disease to more severe stages.
What dietary changes are recommended for managing kidney disease?
Dietary changes can play a significant role in managing kidney disease. Patients are often advised to limit their intake of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, as well as to consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein sources.
How long can you live with kidney disease?
The life expectancy of individuals with kidney disease varies depending on the severity of the disease and the individual’s overall health. However, with proper management, many individuals with kidney disease can live long and healthy lives.
How do you deal with kidney disease?
Dealing with kidney disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare team to manage the disease and maintain overall health. Additionally, support groups and counseling can help individuals cope with the challenges of living with kidney disease.
What foods are bad for kidneys?
Foods that are high in sodium, potassium, and phosphorus are generally considered bad for kidney health. Additionally, processed foods, fast foods, and foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats should also be limited. It’s essential to work with a healthcare team to develop a personalized diet plan that meets individual needs and restrictions.